WTO‘s Committee on Agriculture Held a Meeting to Further Discuss the Outcome of the MC12 Meeting
Time:2022/07/13 BJT
1. Key concerns
At the meeting of the WTO's Committee on Agriculture on 27-28 June 2022, members welcomed the outcomes on food and agriculture achieved at the 12th Ministerial Conference (MC12), and discussed how to implement ministers’ declarations on food security.
In terms of follow-up to the outcomes of MC12, trade ministers at MC12 vowed to collectively address the global food security challenges in the Ministerial Declaration on the Emergency Response to Food Insecurity as well in the Ministerial Declaration on the WTO Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic and Preparedness for Future Pandemics. Members discussed how to develop a dedicated work programme on net food-importing developing countries and least developed countries, but members needed more time to further explore the format and scope of the work programme. Ministerial Declaration on the WTO Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic and Preparedness for Future Pandemics affirms the need to review and build on the lessons learned and challenges experienced in the COVID-19 in order to establish effective food security solutions in preparation for future pandemic responses. At the meeting, the UN World Food Programme (WFP) thanked WTO members for approving the decision to waive export restrictions on WFP's humanitarian food purchases, a decision that WFP said would ensure that critical relief reaches those most in need in a timely manner at a time when global food security is facing unprecedented challenges.
In terms of the pandemic and agriculture, since September 2020, the item on "COVID-19 and agriculture" has been on the Committee's agenda. At the meeting, tmembers addressed additional challenges to food security, including the Russian-Ukrainian conflict, climate change, the impact of extreme weather and the general slowdown in economic growth trends. Some members highlighted the crucial role of trade in ensuring food security and the need to enhance the long-term resilience of agricultural markets, including measures such as avoiding unjustified export restrictions and enhancing transparency. Some members also stressed the importance of unlocking local productive capacity in developing countries to promote long-term food security. Also, as the latest food security challenges were more complex and could not be attributed to the COVID-19 alone, the members also explored whether the title of the standing agenda item "COVID-19 and agriculture" should be changed, but no decision had yet been taken in this regard.
On regular review of agricultural policies, members held discussions on market access, domestic support and export competition policies related to agricultural trade, with reference to China's agricultural input subsidies. This meeting also allowed for detailed communication and understanding of a number of elements related to tariff quota administration, special agricultural safeguards, domestic support and export subsidy notifications. Furthermore, the meeting included discussions on how to enhance transparency of the Agriculture Committee, the Bali Tariff rate quota Decision and the export competition questionnaire responses to the Nairobi Export Competition Decision.
2.Briefing on COVID-19 Pandemic(Issue No.199)
According to WHO statistics, calculated numbers of confirmed COVID-19 cases and deaths reached 547,901,157 and 6,339,899 by 5 July, 2022. The France, the United States, Germany, Italy and Brazil are the five countries (regions) with the highest number of new confirmed cases in the past seven days, and the United States, Brazil, Italy, Russia and Australia are the five countries (regions) with the highest number of new deaths in the past seven days.
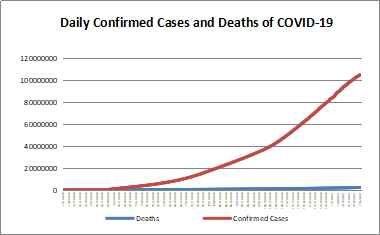
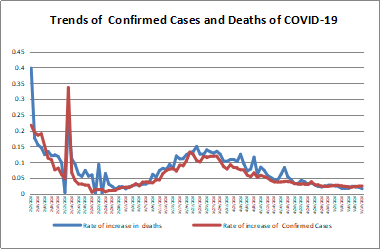
https://covid19.who.int/
The World Bank recently approved the establishment of a new Financial Intermediary Fund (FIF) to prevent, prepare for and respond to future global health threats. The FIF will finance key investments related to COVID-19 to strengthen pandemic prevention, preparedness and response capacity at national, regional and global levels, with a focus on low- and middle-income countries, stimulating increased investment across countries (regions) and enhancing coordination among partners. According to the University of Oxford's online research website Our World In Data, the total number of doses of COVID-19 vaccine administered worldwide had reached 12,120,524,547 by 4 July, 2022. On 30 June, 2022, the World Bank approved the establishment of a new FIF to close critical gaps in countries (regions) in the prevention of, preparedness for and response to COVID-19. The Fund will strengthen national (regional) capacities in areas such as disease surveillance, laboratory systems, health workforce, emergency communication and management, and community engagement. The United States, the European Union, Indonesia, Germany and others have pledged over US$1 billion in support for the fund. Over the next few weeks, the World Bank and the World Health Organization (WHO) will work closely with donors and other partners to develop a detailed plan for the fund, with the goal of launching the fund in the autumn of 2022. In addition to the World Bank Group, the implementing entities for projects financed by the Fund will include the WHO, United Nations agencies, and other organizations. The World Bank will act as the trustee of the FIF, drawing on its financial and legal platform, programme management and operational expertise, and experience in managing the fund, and WHO will also take the lead in supporting and coordinating the work of the FIF's Technical Advisory Group. Moreover, the fund has the flexibility to work through a variety of existing institutions, is inclusive and agile, and operates with a high degree of transparency and accountability.
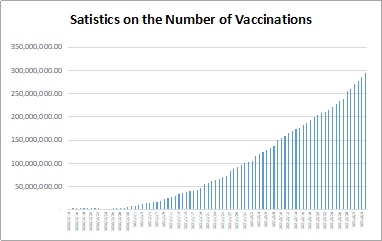
https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinations
In terms of the measures taken by countries (regions) in response to COVID-19, the recent measures taken by countries (regions) have been of varying degrees of leniency, with some countries (regions) gradually relaxing their existing outbreak control measures at various levels, while others have tightened their outbreak control measures. In the Americas, according to data from Johns Hopkins University, as of 17:20 EDT on 5 July, the cumulative number of confirmed cases of COVID-19 in the United States reached 88,001,056 and the cumulative number of deaths reached 1,018,258. In Europe, the Guardian reported another significant increase in confirmed cases in the UK, with the Chief Executive of the UK Health and Safety Executive stating that a further increase in hospital admissions for COVID-19 is expected. According to the Italian news agency Ansa, data from the Italian Ministry of Health show that the cumulative number of confirmed cases in the country has exceeded 18,695,000. As confirmed cases of COVID-19 continue to rise in Spain and France, the Spanish and French authorities are advising their citizens to start wearing masks again in indoor public places. The Russian Federal Service for the Oversight of Consumer Protection and Welfare said on 1 July that Russia would suspend previously adopted restrictive measures against the pandemic, including a mask wearing system, a ban on nighttime meals and a number of other measures, in light of the continued decline in the intensity of the COVID-19, but also noted that restrictive measures may be reinstated if the COVID-19 pandemic worsens. In Asia, according to a report by KBS World Radio, the South Korean government will follow up 10,000 people over three years in order to investigate the aftereffects of COVID-19. The government will analyse the existence of the aftereffects of COVID-19 through three years of observation and investigation, assess the risk factors that have an impact on the development of the aftereffects, and formulate appropriate management guidelines that will be used to deal with other possible future The survey will be used to assess the risk factors for the aftereffects of the disease, to formulate appropriate management guidelines, and to respond to other infectious diseases that may arise in the future. According to a report by the CLS news agency, as of 18:00 local time on 5 July, Japan had 36,189 new confirmed cases of COVID-19 on that day, with a cumulative total of 9,456,796 confirmed cases; 20 new deaths, with a cumulative total of 31,352 deaths. Against the backdrop of a possible seventh wave of COVID-19 outbreak in Japan as new cases rebound daily across the country, the Japanese government is taking an increasingly cautious approach to launching tourism promotion.


