IMF Issued a Commentary to Call for Resisting Geoeconomic Fragmentation
Time:2022/06/02 BJT
1. Key concerns
On May 23, 2022, International Monetary Fund (IMF) issued a commentary on the sharp rise in the risk of geoeconomic fragmentation, the weakened capacity of societies to cope with risk and the hindrance of global integration processes. Tensions over trade, technology standards and security have been growing, undermining the growth and trust in the current global economic system. According to the commentary, four priorities need to be considered to address the disintegration crisis.
The conflict in Ukraine has compounded the Covid-19 pandemic, dragging down growth, and pushing up inflation. High food and energy prices are weighing heavily on households around the world. Tightening financial conditions are putting further pressure on highly indebted nations, companies, and families. And countries are re-evaluating global supply chains amid persistent disruptions. All these changes have caused the sharply increased risk of geoeconomic fragmentation.
Uncertainty around trade policies alone reduced global gross domestic product in 2019 by nearly 1 percent, according to IMF research. And since the war in Ukraine started, around 30 countries have restricted trade in food, energy, and other key commodities.
Reconfigured supply chains and higher barriers to investment could make it more difficult for developing nations to sell to the rich world, gain know-how, and build wealth. Advanced economies would also have to pay more for the same products, stoking inflation. And productivity would suffer as they lost partners who currently co-innovate with them. IMF research estimates technological fragmentation alone can lead to losses of 5 percent of GDP for many countries.
To prevent further deterioration of the above situation, the comments pointed out that to restore trust in the global system, four priorities need to be considered. First, strengthen trade to increase resilience, diversify imports and exports, and supply supportive policies to improve business environment. Second, step up joint efforts to deal with debt. With roughly 60 percent of low-income countries with significant debt vulnerabilities, a return to debt sustainability will draw new investment and spur inclusive growth. Third, modernize cross-border payments. Countries can work together to develop a global public digital platform - a new piece of payment infrastructure with clear rules. Fourth, confront climate change - the existential challenge, closing the gap between ambition and policy.
In addition, multilateral institutions can also play a key role in reshaping global cooperation and resisting fragmentation, including further strengthening their governance to ensure they reflect changing global economic dynamics. Multilateral institutions can also leverage their convening power, and maximize use of their diversified toolkits. For example, IMF can help with its range of financial instruments, bilateral and global surveillance and even-handed approach across its membership.
2.Briefing on COVID-19 Pandemic(Issue No.193)
According to WHO statistics, calculated numbers of confirmed COVID-19 cases and deaths reached 523,786,368 and 6,279,667 by May 24, 2022. The US, China, Australia, Germany and Japan were the five countries (regions) with the highest number of new confirmed cases in the past seven days. The US, China, Australia, Germany and Japan were the five countries (regions) with the highest number of new deaths in the past seven days.
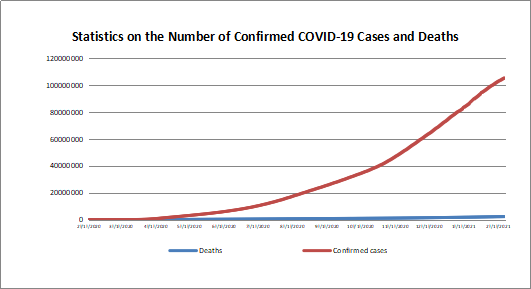
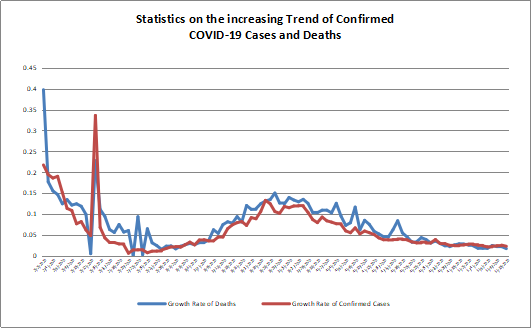
https://covid19.who.int/
The World Health Organization (WHO) issued an emergency use listing (EUL) for the adenovirus-vectored COVID-19 vaccine CONVIDECIA, which is the 11th vaccine has been validated by WHO for emergency use, manufactured by CanSino Biologics, China. Statistics from Our World in Data, an online research site of the University of Oxford, presented that 11,791,615,574 doses had been administered globally by May 24, 2022. On May 19, 2022, WHO issued an EUL for the adenovirus-vectored COVID-19 vaccine CONVIDECIA, which is the 11th vaccine has been validated by WHO for emergency use, manufactured by CanSino Biologics, China. CONVIDECI is a single-dose adenovirus-vectored COVID-19 vaccine that can be used for people over the age of 18. CONVIDECIA was assessed under the WHO EUL procedure based on the review of data on quality, safety, efficacy, a risk management plan, programmatic suitability and a manufacturing site inspection conducted by WHO. EUL procedure assesses the suitability of novel health products during public health emergencies. The objective is to make medicines, vaccines and diagnostics available as rapidly as possible to address the emergency while adhering to stringent criteria of safety, efficacy and quality. The assessment weighs the threat posed by the emergency as well as the benefit that would accrue from the use of the product against any potential risks. As part of the EUL process, the company producing the vaccine must commit to continue to generate data to enable full licensure and WHO prequalification of the vaccine. The WHO prequalification process will assess additional clinical data generated from vaccine trials and deployment on a rolling basis to ensure the vaccine consistently meets the necessary standards of quality, safety and efficacy for broader availability.
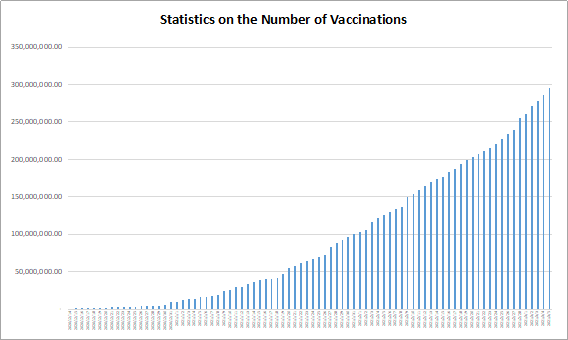
https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinations
In terms of the restrictions taken by countries (regions), there are different levels of measures adopted against COVID-19. Most countries (regions) are gradually relaxing their previous pandemic restriction measures to different levels, or implementing new policy on fighting against the pandemic. In America, the US is facing a shortage of funds to deal with the COVID-19 pandemic, according to ABC. The shortage of funds could affect the ordering of vaccines, which could lead to a shortage of vaccine supplies in the US this autumn. In March the US government asked Congress for an emergency allocation of US$ 22.5 billion for pandemic preparedness, and Congress reduced the amount to US$ 10 billion. In Europe, the Spanish Ministry of Transport issued a statement on May 21 allowing all tourists to enter Spain with a negative 72-hour nucleic acid test certificate. On May 19, the Germany’s Constitutional Court ruled to allow mandatory COVID-19 vaccination for care and health workers, rejecting a complaint against the injunction. In Oceania, the New Zealand’s COVID-19 Response Minister, Chris Hipkins, announced a new version of the My Vaccine Pass, which will be available for download from May 24 for residents who need it. The new My Vaccine Pass will show the status of the COVID-19 vaccination booster. In Asia, According to Yonhap News Agency on the 20th, the implementation of "no quarantine for COVID-19 patients", which was planned to be implemented on the 23rd in South Korea, will be postponed due to the discovery of a mutated strain of the more infectious new COVID-19 virus. The current compulsory seven-day quarantine measure for COVID-19 patients will be extended for four more weeks. On May 13, the Deputy Prime Minister Vu Duc Dam issued the Prime Minister's Circular No. 416 on suspending the requirement for COVID-19 testing before entry into Vietnam, according to the Vietnam News Agency. In order to implement the restriction measures to prevent and control the pandemic while creating convenient conditions to promote economic and social activities, the Prime Minister instructed to suspend the requirement for people to be tested for the COVID-19 before entering Vietnam from 00:00 on May 15. The Ministry of Health will pay close attention to the pandemic situation and will provide timely guidance on appropriate measures to prevent and control the pandemic.


