FAO Published Statistical Yearbook 2021 in the Times of Crisis
Time:2021/11/16 BJT
1. Key concerns
Recently the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) published its Statistical Yearbook 2021. The Statistical Yearbook 2021 is divided into four thematic chapters: Chapter 1 (Economic dimensions of agriculture) provides an overview of agriculture, forestry and fishing from an economic standpoint. Chapter 2 (Production, trade and prices of commodities) presents the outputs of the sector in terms of the production and trade of the different commodities and the evolution of prices. Chapter 3 (Food security and nutrition) looks at how some of these outputs are consumed by narrowing the focus on food security and nutrition. Chapter 4 (Sustainability and environmental aspects of agriculture) deals with the impacts of the sector as a whole on the environment. Each chapter draws on the latest available data to describe through text and charts the trends since the early 2000s.
In terms of economic dimensions of agriculture, the share of agriculture in global GDP has been stable at around 4% since 2000. Agriculture value added went up 73% between 2000 and 2019, to around USD 3.5 trillion. Agriculture employed 874 million people in 2020, or 27% of the global workforce, compared with about 1050 million (or 40%) in 2000. Pesticide use went up 36% between 2000 and 2019, but has plateaued since 2012.
In terms of production, trade and prices of commodities, the production of primary crops was 9.4 billion tonnes in 2019, 53% more than in 2000. Four crops account for about half of global primary crop production: sugar cane, maize, wheat and rice. The production of vegetable oils more than doubled between 2000 and 2019, driven by a sharp increase in palm oil. 337 million tonnes of meat were produced in 2019, 44% more than in 2000, with chicken meat representing more than half the increase.
Despite the increasing food production, the global level of undernourishment has risen sharply between 2019 and 2020, from the breaking out of the COVID19 pandemic. There are almost 770 million people undernourished globally in 2020, close to 118 million more than in 2019. In terms of geographic distribution, while most of the undernourished people live in Asia, Africa has the highest prevalence of undernourishment.
In the last chapter on sustainability and environmental aspects of agriculture, the yearbook indicated that between 2000 and 2019, agricultural land declined by 127 million ha - roughly the size of the Niger - while forest area declined by 94 million ha – about the size of the United Republic of Tanzania. Greenhouse gas emissions on agricultural land declined by 2%, but farm-gate greenhouse gas emissions went up 11%. Around 55% of them are related to livestock.
2. Briefing on COVID-19 Pandemic(Issue No.163)
According to WHO statistics, calculated numbers of confirmed COVID-19 cases and deaths reached 249,743,428 and 5,047,652 by November 9, 2021. The U.S., Russia, the UK, Turkey, and Germany were the five countries (regions) with the highest number of new confirmed cases in the past seven days. The U.S., Russia, Ukraine, Romania and India were the five countries (regions) with the highest number of new deaths in the past seven days.
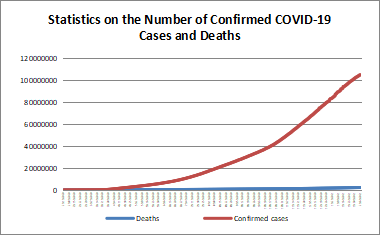
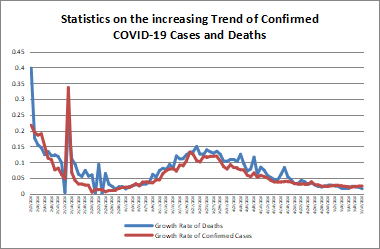
数据来源:https://covid19.who.int/
International Monetary Fund, World Bank Group, World Health Organization and World Trade Organization met to discuss strategies to accelerate the supply and deployment of COVID-19 vaccines. Statistics from the WHO’s website presented that 7,084,921,786 doses had been administered by November 9, 2021. October 30, 2021, local time, the heads of the International Monetary Fund, World Bank Group, World Health Organization and World Trade Organization met in Roma to discuss strategies to accelerate the supply and deployment of COVID-19 vaccines, especially in low- and lower-middle-income countries, and issued a joint statement. The joint statement stated that of the 7 billion vaccine doses administered globally, only 35 million doses, or 0.5%, have been administered in low-income countries. In advanced economies, over 60% of the population is fully vaccinated, with some now receiving booster shots, while less than 2% of the population in low-income countries is fully vaccinated.
The joint statement indicated that the pandemic remains the biggest risk to economic health, and its impact is made worse by unequal access to Covid-19 vaccines, tests, treatments, and personal protective equipment. That’s why we need to reach the global targets to vaccinate at least 40% of people in every country by the end-2021, and 70% by mid-2022. To bring an end to the pandemic, the G20 needs to accelerate existing dose donations to COVAX (the vaccines pillar of the Access to COVID-19 Tools Accelerator), eliminate export restrictions on vaccines and critical inputs, build collective accountability. At the same time, countries (regions) must be ready and able to deploy vaccines when they arrive. At last, the joint statement warned that urgent action is needed now. A failure to act could mean COVID-19 will have a prolonged impact into the long-term, which could reduce global GDP by a cumulative $5.3 trillion over the next five years and lead to five million additional lives lost.
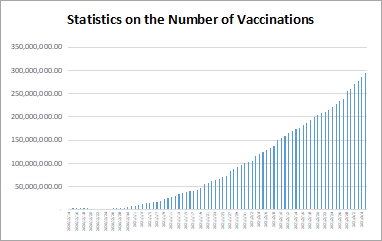
数据来源:https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinations
In terms of the restrictions taken by countries (regions), the pandemic prevention policies in different continents are still implemented. In America, U.S. announced the Covid-19 travel restrictions which was implemented from the beginning of 2020 will be lifted starting November 8. The fully vaccinated international travellers from most of the countries (regions) are welcomed to visit the U.S.. In Europe, the Secretary of State of the UK, in the exercise of the power under regulation 39A of the Medical Devices Regulations 2002 and, in circumstances which give rise to a need to protect the public from a risk of serious harm to health, has decided to permit the placing on the market of the COVID-19 test devices. According to the protocol, the product which has not been validated under Regulation 38A(5) is permitted in the white list of exemptions in appropriate circumstances and for a specified period of time that there is a serious health risk. In Oceania, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) of Australia officially recognized China’s Sinopharm and India’s Covaxin vaccine. Hundreds of thousands of international students, Australian citizens and family members who have been vaccinated with the two Covid-19 vaccines are expected to return due to the approval. In Asia, Japan announced that the entry ban implemented against COVID-19 would be lifted starting November 8. The business travellers, international students and interns will be allowed to enter, and the quarantines of the business travellers and labourers who were vaccinated will be shortened from 10 days to 3 days.


