The Pandemic Continues to Impact Global Supply Chains, Which May Exacerbate obstacles to fulfilling contractual obligations of International Trade in Goods
Time:2021/09/16 BJT
1. Key Concerns
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to impact global supply chains. The current international freight rates remain high, the container shortage and port congestion have not yet been alleviated, and the shortage of labor has further complicated the matters. After the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, the obstacles to international freight and the soaring of shipping costs have caused major disruptions to international trade in goods, triggering a supply chain crisis in many countries (regions); As the surging COVID-19 variants in 2021, the problem on the global supply chain that had not fully recovered keeps getting worse. One such example is the semiconductor (chip), Fitch Ratings estimated on September that the DELTA variant would continue to disrupt chip production in Asia. An overall improvement in the global supply of chips from mid-2022 is expected, whereas chip shortage will last until mid-2023.
Many companies made pessimism forecast on the outlook of the supply chain. Hsieh Huey-chuan, president of Taiwan-based Evergreen Marine, said that port congestion and a shortage of container shipping capacity may last into the fourth quarter or even mid-2022 at an investor briefing on August 20.
The transportation company DHL also believed that increasing supply chain disruption will persist through 2022. In addition, American big retailers Walmart and Home Depot announced they were purchasing shipping containers and chartering private vessels for their goods. The The apparel retailer American Eagle Outfitters also acquired logistics company AirTerra in August.
The Pandemic continues to impact the international trade order, and the disruption of supply chain is the primary obstacle to fulfill the contractual obligations of International Trade in Goods. Under this circumstance, the problems of raw materials supply, labour, transportation may cause a delay or failure to deliver, resulting in disputes of international trade.
2. Briefing on COVID-19 Pandemic
According to WHO statistics, the cumulative numbers of confirmed COVID-19 cases and deaths reached 224,511,226 and 4,627,540 by September 13, 2021. The U.S., the UK, India, Iran and Turkey were the five countries (regions) with the highest number of new confirmed cases in the past seven days. The U.S., Russia, Mexico, Iran and Indonesia were the five countries (regions) with the highest number of new deaths in the past seven days.
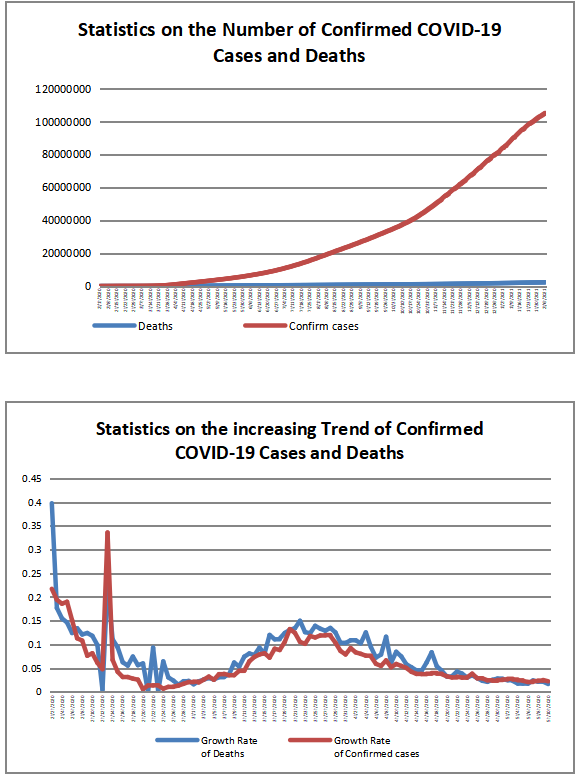
https://covid19.who.int/
The production capacity of the COVID-19 vaccine have been increased, and the process of the COVID-19 vaccination has been accelerated. Statistics from Our World In Data, an online research site of the University of Oxford, presented that 5,734,786,152 doses of the COVID-19 vaccine had been administered on September 12, 2021. The International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers & Associations (IFPMA) stated in early September that the overall COVID-19 vaccine manufacturing output will pass the 7.5 billion dose mark this month, and the global production of vaccine does is projected to reach 12 billion by the end of 2021. Israel’s Ministry of Health said on September 12 that it was actively preparing to offer a fourth dose of COVID-19 vaccines. According to a report. Israel has administered third doses to people from August 2021. Statistics released by the Japanese government on September 13 showed that 50.9% of the population has been administered two doses of COVID-19 vaccines, and 63.0% of the population has been administered the first dose.
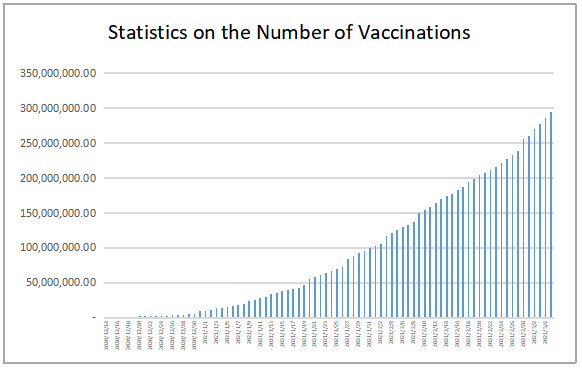
https://ourworldindata.org/covid-vaccinations
The restrictive measures are taken by countries (regions) are further differentiated. In the Asia-Pacific region, some countries have relaxed the restrictive measures. The Aviation Authority of Vietnam is planning to resume the domestic airlines, and the city of Hanoi, Vietnam imposed various levels of restrictive measures based on the risk levels of the pandemic. The Kazakhstan government increased the number of international flights. South Korea will expand incentives to those who have fulfilled the vaccination procedure and will consider simplifying restriction measures. In Europe, some countries (regions) are tightening the quarantine regulations for entry, and in the meantime, easing their domestic restrictions. As a result of the increase of new confirmed cases in Europe, Lithuania, Estonia, Belgium, Czech Republic, Denmark, Romania and other countries have narrowed the scope of countries (regions) whose residents will be exempt from quarantine entry, and imposed stringent quarantine entry regulations. Denmark has lifted all domestic restrictions after more than 70% of its population fulfilled the COVID-19 vaccination. According to Russia's Covid headquarters, Russia will resume passenger flights with Spain, Iraq, Kenya and Slovakia from September 21. In the Americas, the U.S. government released the COVID-19 Action Plan to accelerate vaccination against COVID-19 and impose strict pandemic prevention requirements for employers. Staff of Federal government are required to be vaccinated by presidential decree, and vaccination of medical staff be included in medical insurance and subsidies are required. In Africa, as a result of COVID-19 vaccination promotion and pandemic mitigation, some countries (regions) have relaxed the restrictive measures. On September 12, the President of South Africa announced to ease pandemic restriction measures and planned to launch the COVID-19 vaccination pass. The governments of Botswana and Zimbabwe have successively decreased the level of restriction.

