【ICDPASO】WHO Approved China’s Sinovac COVID-19 Vaccine for Emergency Use; Multiples International Agencies Promoted the Economic Recovery in Developing Countries
Time:2021/07/27 BJT
1. Current Work Progress
Please scan the QR code below for the complete version of global pandemic situation and the corresponding measures of relevant countries (regions),.

2. Information of Relevant Measures for the Pandemic
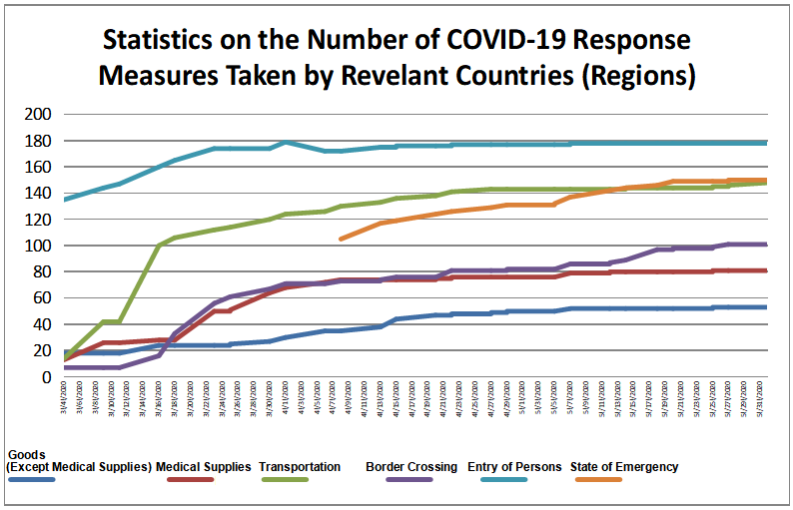
2.1 Measures Taken for Trade in Goods (Except Medical Supplies)
Due to the influence of COVID-19 and other factors, some countries (regions) have taken restrictive measures on the import and export of goods. Up to June 2, there are 90 countries (regions) that have taken actions to trade in goods. Among them, Vietnam will suspend imports of pigs from Thailand from June 30, 2021.
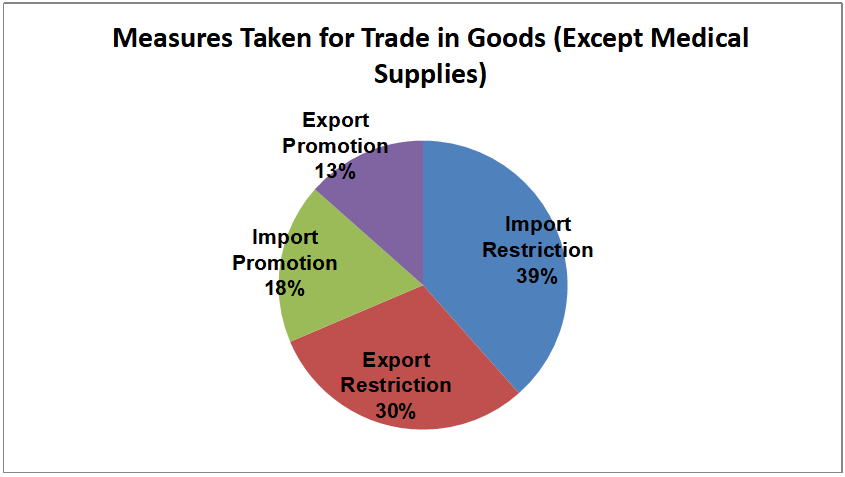
2.2 Measures Taken for Trade in Medical Supplies
Most of countries (regions) have actively launched COVID-19 vaccine to control the pandemic. As of June 2, 109 countries (regions) adopted measures related to trade in medical supplies. Singapore will permit private agencies to import COVID-19 vaccines which are approved by WTO for emergency use; Russia launched the world’s first animals COVID-19 vaccine; Zambia, Lebanon, Panama, Serbia, Mexico, and the United Kingdom urgently approved COVID-19 vaccine; and Finland suspended the use of Johnson & Johnson's COVID-19 vaccine.
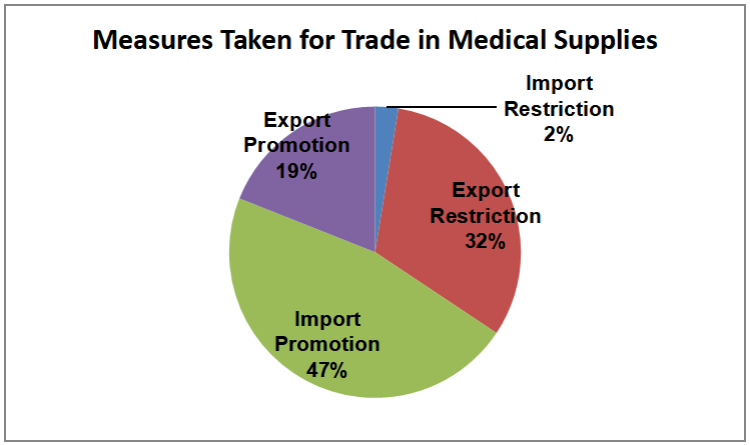
2.3 Measures Taken for Transportation
The situation of COVID-19 in Southeast Asia raised global concerns, with several countries extending or maintaining restrictive measures on international flights. As of June 2, 178 countries (regions) have taken relevant measures for transportation vehicles. Vietnam, the United Arab Emirates, Myanmar and India extended their restrictions; Hong Kong, China designated Cambodia, Thailand and Vietnam as Group B high-risk areas; Algeria and Russia resumed a part of international flights.
2.4 Measures Taken for Border Crossing
In response to the spread of COVID-19 virus variant, most countries (regions) maintained controls of border crossing. By June 2, 133 countries (regions) have taken relevant measures.
2.5 Measures Taken for the Administration of Entry of Persons
According to the COVID-19 pandemic situation, some countries (regions) have constantly adjusted their entry restrictive measures. Up to June 2, 198 countries (regions) have taken relevant measures. Lithuania relaxed the entry restrictions for Cypriot and Swedish travelers; Hungary and Moldova mutually lifted travel restrictions on each other's vaccinated citizens; Norway began to provide special entry quarantine measures for its military personnel and those of its Allies; Ireland and Denmark relaxed some entry quarantine requirements; Iceland announced that visitors receiving COVID-19 vaccine produced by Sinopharm would not be quarantined; Laos, Japan, Macao, Greece, Italy and Spain extended their entry bans to varying degrees. Latvia's Ministry of Transportation called on the government to raise the standard of entry quarantine.
2.6 The Declaration of the Country’s State of Emergency
With the continuous promotion of COVID-19 vaccination, most countries (regions) have been relaxing some of the prevention measures to mitigate the adverse socio-economic impact of the pandemic. Up to June 2, 181 countries (regions) have taken relevant measures.Turkey, Israel, Japan, Spain and Sweden relaxed their restrictions; Mumbai, India allowed some retail stores to open conditionally; the Palestinian President announced an extension of the current state of emergency for another month.
3. Current Global Response to the Pandemic
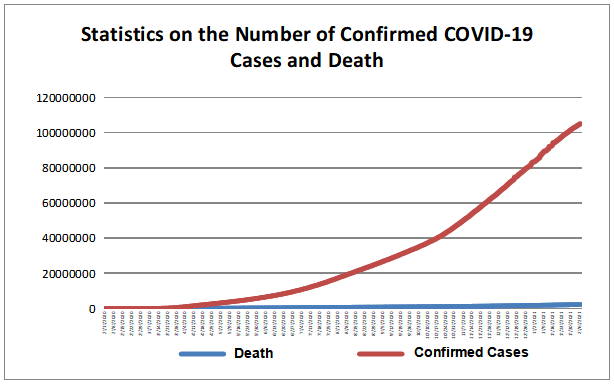
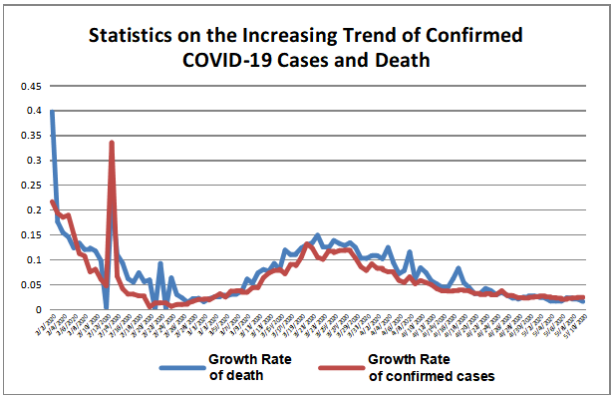
The growth of confirm cases of COVID-19 decelerated globally; WHO labeled new variants of COVID-19. According to WHO statistics, diagnosed cases of the COVID-19 pandemic reached 170,812,850 and 3,557,586 cases died by June 14, 2021. India, Brazil, Argentina Colombia,and the U.S. were the five countries (regions) with the highest number of new confirmed cases in the past seven days. India, Brazil, the U.S., Colombia and Argentina,were the five countries (regions) with the highest number of new deaths in the past seven days.
The latest weekly report of WHO showed that for the week ending May 30, there were more than 3.5 million new confirmed cases around the world, a decrease of 15 percent over the previous week, and about 78,000 new deaths, down 7 percent from the previous week.
At the 74th World Health Assembly, WHO announced the use of the Greek alphabet for labeling the major variants of COVID-19, with the aim of avoiding stigmatization by associating the pandemic with the country where it was first discovered.
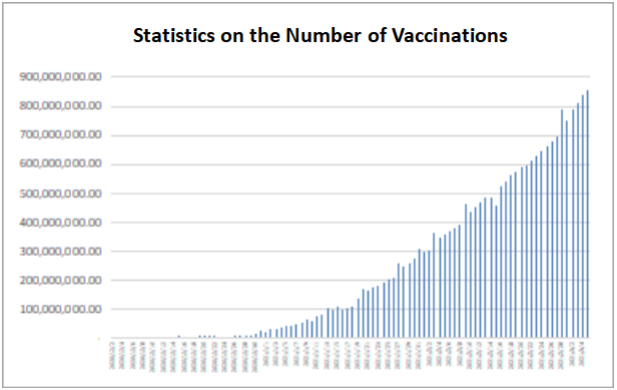
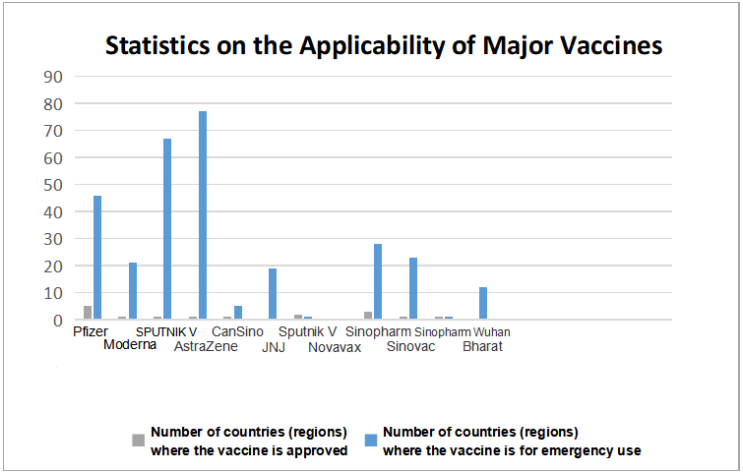
WHO approved the emergency use of China’s Sinovac COVID-19 vaccine; international agencies promoted the economic recovery in developing countries. On June 1, 2021, WHO announced to put Sinovac COVID-19 vaccine in “Emergency Use List”. In the announcement, WHO indicated that Sinovac COVID-19 vaccine met international standards for safety and efficacy.
On the same day, four major international institutions - IMF, WB, WHO and WTO - called for an urgent global investment of $50 billion to advance equitable distribution of public health tools, accelerate the end of the pandemic, and lay the foundation for global economic recovery and public health security.
As the pandemic disrupted the Global Labor Market continuously, the International Labor Organization (ILO) proposed recovery strategies. ILO pointed out that COVID-19 pandemic has caused profound damage on global labor markets and led to increased regional and demographic inequality, intensified poverty and reduced job opportunities. Job losses and compressed working hours have led to a sharp decline in labor income and an increase in poverty.
ILO proposed the following recovery strategies: promoting the growth of basic economy and supporting the productive employment; promoting the transformation of household income structures and labor markets; supporting inclusive, sustainable and resilient growth and development of the economy, and laying a solid institutional foundation for economic growth; strengthening social protection and social dialogue to develop a people-centered recovery strategy.







